CSS: What happened in 2020?
The year 2020 has been a year to remember, but there have
also been many themes and elements that you surely prefer to forget. We
have had pandemic, natural disasters, social and personal
disasters. If any of these problems have affected you, here I send you a
lot of strength!
Forget CSS, learn CSS
One of the topics that you should also forget, or want to
forget or reconsider, is related to everything you knew about CSS before
2020 - and a good part of 2019.
It turns out that in 2020 the CSS, Content Style Sheets,
or cascading style sheets in Spanish has stopped looking like what
you have been implementing for years in your web site and application development
projects.
Some examples
If before you were used to using CSS breakpoints to
make the content of your website respond according to the width of
the device, now you can take advantage of the Grid properties, CSS Grid to
create dynamic and responsive templates for the same effect, and
with fewer lines of code.
You could also use CSS-in-JS to place your styles
in your components. This way you don't have to rely on global
style sheets and you can develop themeable design systems.
In the same way, Tailwind CSS has established
itself in 2020, in the sector, thanks to its use of “ utility-first” CSS,
encouraging to reconsider the use of famous and powerful frameworks,
and also to reconsider the use of names! of semantic classes! : or
New features and adoption
Let's look together at some of these developments from the
world of CSS and its adoption in 2020, building on the 2020 State of CSS survey
conducted by Sacha Greif and Raphël Benitte. In addition,
we will review what some of them mean for your web development processes with
CSS.
 |
| Chart 2020.stateofcss.com |
According to the Greif & Benitte survey, adoption of the
new features is lagging a bit as the community absorbs the new properties.
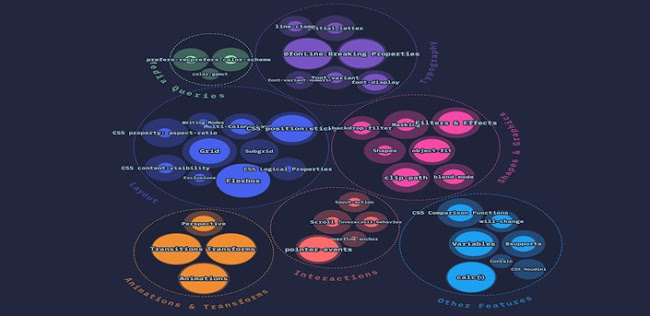
Media Queries
Among 3 of the Media Queries properties that you
probably don't know, prefers-color-scheme, prefers-reduced-motion, and color-gamut prefers-color-scheme is
the best known among developers and is also the most used with a ratio of
35.3%.
What is each of these properties for?
Prefers-color-scheme
The prefers-color-scheme feature of media
queries are used to detect whether the user has requested that the system
use a light or dark color theme.
Prefers-reduced-motion
The prefers-reduced-motion function of media
queries are used to detect whether the user has requested that the system
minimize the amount of nonessential motion it uses.
Color-gamut
The color-gamut property can be used to test the approximate gamut of colors supported by the user agent and the
output devise.
Typography
Regarding typography, properties such as @ font-face or line
break properties are still the most used such as the font-display
property, which has a usage rate of 69.2%. Properties such as line-clamp,
or font-variant do not reach a 50% ratio.
Let's take a look at what they mean!
@ font-face
@ font-face is a CSS at-rule ( at-rule )
that specifies a custom font to display text with; the font can be loaded
from a remote server or from a font installed locally on the user's
own machine.
Line break properties
The line break property sets how to break lines of
Chinese, Japanese, or Korean text when working with punctuation marks, for
example.
Font-display
The font-display descriptor determines how a font is displayed based on whether it is downloaded and ready to use.
Layout and templates
According to the survey, Flexbox is still the best
known and most used property with a ratio of 98%, but properties like Grid,
as we have mentioned before, also deserve your attention since they have a
utilization ratio of 74.1%. Property position: sticky with
utilization ratio 81.4%, or the property of multi-column layout
( multi-column layout ) with use ratio of 59.2. Other
properties such as exclusions, writing modes, subgrid, or CSS
logical properties do not reach 50% usage.
Let's review what are some of the most important features.
Grid
CSS Grid Layout stands out for dividing a page into
main regions or defining the relationship in terms of size, position, and layer
between parts “of a control built from HTML primitives”.
Flexbox
CSS Flexible Box Layout is a CSS module that defines a
CSS box model optimized for user interface layout and element layout in one
dimension. In this model, the children of a flex container can be
positioned in any direction and their sizes can be “ flexed ”,
growing to fill unused spaces or shrinking to avoid overflowing the parent.
Multi-column Layout
CSS Multi-column Layout is a CSS module that adds
support for multi-column layouts and templates. Support is
included for setting the number of columns in a layout, as well as how content
should flow from one column to another, and the sizes of the spaces between
columns and column dividing lines.
Position: sticky
The CSS position property sets how an element
is placed in a document. The top, right, bottom, and left properties determine
the final location of positioned elements. An element with position:
sticky is positioned according to the user's scroll position.
Shapes and graphics
Regarding shapes and graphics, filters and effects are
the most used with a utilization rate of 73.4%, but properties such as object-fit (80.1%), clip-path (61.1%), blend-mode ( 55.3%) ) or backdrop-filter (52.9%) also
have a lot of weight in the community.
Let's review what are some of the most important features.
Object-fit
The object-fit CSS property sets how the
content of a replaced element, such as an <img> or
<video> , should be resized to fit its container.
Filters and Effects
The filter property of CSS applies graphic
effects such as blur or color change to an element. Filters are used to
adjust images, backgrounds, or borders.
Clip-path
The clip-path property creates a clipping
region that sets how much of an element to display. The parts that are
within the region are displayed, while the parts that are outside are hidden.
Blend-mode
The CSS data type <blend-mode> describes how
colors should appear when elements overlap. It is used in the background-blend-mode and mix-blend-mode
properties.
Animations and Transformations
The Transitions (95.5%), Transformations (95.7%)
and entertainment (92.7%) remain very important in the modern web
development. The perspective is a bit far away , with a
utilization ratio of 61.2%.
Let's remember what exactly these properties are.
Transitions
The CSS Transitions module is a module that allows you to
create gradual transitions between the values of specific CSS
properties. You can control the behavior of these transitions by
specifying their timing, duration, and other attributes.
Transformations
CSS Transforms is a module that defines how elements
designed with CSS can be transformed into a two-dimensional or
three-dimensional space.
Animations
CSS Animations is a module that allows you to animate
CSS property values over time, using keyframes. You can control these
animations by specifying their timing, duration, number of repetitions, etc ...
Interactions
In the interactions section, the pointer-events
property is clearly the most important with a use rate of 85.1%, while other
properties such as touch-action, scroll-snap, event-scroll-behavior, or overflow-anchor do
not reach the 50% usage.
If you don't remember what exactly these properties are, we
can go over them.
Pointer-events
The pointer-events property establishes under what
circumstances a graphical element can become the target of pointer-events.
Scroll Snap
CSS Scroll Snap is a CSS module that introduces
scroll snap positions, which enforce scroll positions. Look at
these examples. You will see that with scroll-snap you can lock
the viewport on certain elements or locations after a user has finished
scrolling.
Other features
calc () continues to have a fairly high usage with a
94.2% utilization rate, but other features such as variables (78.5%), will-change (63.6%), CSS
comparison functions (57.9%), @supports (57.3 %). Far is
the Contain property (34.2%), and even worse the CSS
Houdini (5.7%).
What do some of these properties mean?
Variables
CSS Custom Properties for Cascading Variables is a module that allows the creation of custom properties that can be used more than
once.
Will-change
The will-change property tells browsers how an
item is expected to change. Browsers can configure optimizations before an
item is changed.
CSS Houdini
CSS Houdini is a set of low-level APIs that
exposes parts of the CSS engine, giving developers the power to extend CSS, by
connecting with the layout and design process of a browser's rendering
engine. Houdini allows you to create new CSS functions without
waiting for them to be implemented natively in browsers. You can learn
more about Houdini in the Mozilla documentation.
Conclusion
These are just some of the properties, and changes that CSS
has undergone in recent years and especially in 2020. If you have been working
with CSS for years, I recommend you review them well (at the browser
compatibility level ) and do tests before implementing them in your
projects in production.
I think these new properties add a lot of value to web
development and the CSS language, especially because they help reduce
verbosity. I also think that the CSS community should rethink the true usefulness of some of these properties at a general level, since some of them
are either not known to web developers or not used.
However, if you are a developer, I encourage you to try them
and if possible, to improve them, because as you can see, CSS is an increasingly dynamic graphic design language and this is thanks to you.












No comments
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.