PHP 8: What's new? | Php 8 features
On November 26, 2020, the PHP 8 release date so the PHP developer the community celebrated the launch of one of the most anticipated versions of the programming language in recent years: PHP 8. So in this article, I will discuss PHP 8 and give the answer to these questions PHP 8 new features, What changed in PHP 8? Is PHP 8.0 stable? and What is new in the latest version of PHP? and this article is a complete PHP 8 review that will give you information about all you need to know about PHP 8. So let's discuss the topic PHP 8 what is new PHP 8 features.
 |
| Php 8 what is new |
PHP 8 - Released
It is an important update according to php.net,
because it contains "new resources and optimizations that include named
arguments, union types, attributes, promotion
of constructive properties, match expressions, the
nullsafe operator," the much desired JIT compiler,
"improvements in the type system, error handling ”, etc, etc ...
The truth is that these new resources excite me, and
you? Are you still thinking that PHP is dead, or thinking about the
future it has as a programming language?
Let's look at 8 of these new PHP 8 resources together, we will compare how you had to program certain functionality in PHP 7 and how you will do it now in PHP 8.
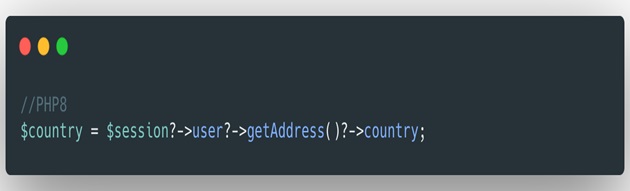
1. The Nullsafe Operator ( RFC )
One of the problems with the null-merge operator is that it
doesn't work on method calls. You need, for example, intermediate checks
and if in PHP 7 you had to check for null conditions, which could be infinite
and sometimes absurd, now you can use a chain of calls with nullsafe,
and have a behavior similar to null fusion in the methods. If
the "evaluation of an element fails, the execution of the entire string is
addressed, and the string is evaluated as null".
Note to self: if this doesn't excite you, you don't
need to read on. But look at the example from php.net:
Checking for null conditions in PHP 7
Nullsafe operator in PHP 8
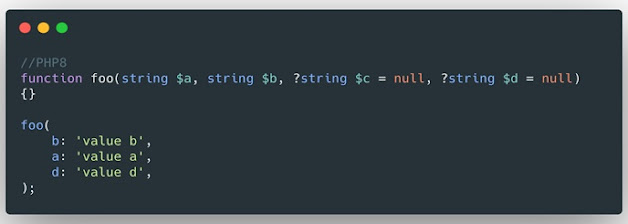
2. Named arguments ( RFC )
Named arguments allow you to pass values to a function,
specifying the name of the value. This way you can forget about the order
and omit optional parameters. Furthermore, the arguments are automatically
documented. Look at the example:
Mandatory parameters in PHP 7
Optional parameters with named arguments in PHP 8
Another example of optional
parameters with named arguments in PHP 8
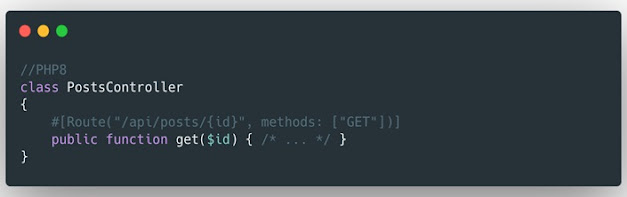
3. Attributes ( RFC )
Attributes in PHP are what in other languages, or frameworks, are
known as annotations . PHP 8 and allows you to add structured
metadata with native PHP syntax to classes, instead of PHPDoc
annotations. What do you think?
Annotations in PHP 7
Attributes in PHP 8
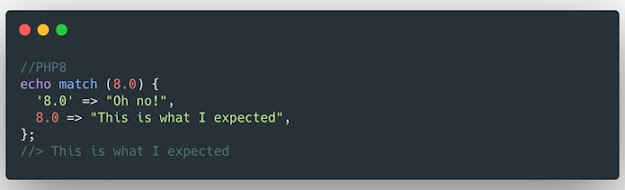
4 match expressions ( RFC )
Match expressions can be seen as the brother or
sister of the switch expression , since they are similar
expressions. Match expressions can be stored as variables or
returned (they can return values), they don't need interrupt- break trades,
they can combine conditions, they do strict type comparisons, and they don't do
any kind of coercion. Look at this example:
Switch expression in PHP 7
Match expression in PHP 8
5. Promotion of constructive properties ( RFC )
The "promotion of constructive properties" adds
"syntactic sugar" to create valuables or data transfer
objects. Now you can combine class properties and a constructor for them
all in one. As you can see in the example below, we are talking about less
boilerplate code "to define and initiate a property". How about?
Properties and constructor in PHP 7
Properties and constructor in PHP 8
6. JIT compiler (dynamic translations)
The JIT compiler - just in time - promises
great improvements at the performance level. But you should know that not
always within the context of web requests. With PHP 8 you have 2 JIT
compilation engines: Function JIT and Transit JIT , with
Transit JIT the one with the best performance, 3 times better
in synthetic benchmarks in some types of applications.
Look at the following comparison:
Comparison of PHP 8 without JIT, with Tracing JIT and with Function JIT
7. Types of union ( RFC )
Union types can be useful in many cases, due to the dynamic
type nature of PHP. Union types are a collection of two or more types
indicating that either of the two can be used. Instead of combining types
in annotations in PHPDoc , you can use a native binding
declaration type and this is valid at the time of execution.
Types in annotations in PHPDoc of PHP 7
Native union type declaration in
PHP 8
Note that void can
never be part of a union type, as it indicates "no return value".
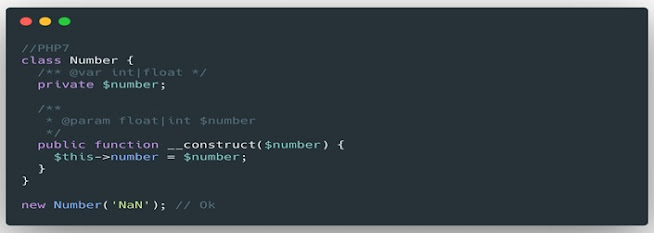
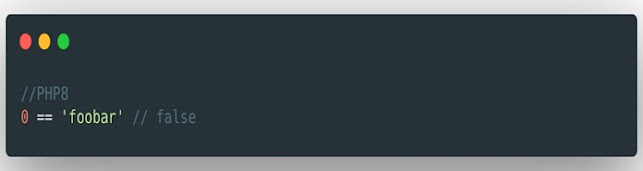
8. Smart comparisons between strings and numbers ( RFC )
This RFC solves the case where in PHP 0 ==
“foo” is true. Now when you compare to a numeric string, PHP 8 uses a
numeric comparison. If not, convert the number to string and
use string comparison.
Confusing comparison in PHP 7
Smart comparison in PHP 8
The resources discussed in this article are just some of the
improvements that PHP 8 brings. There are many others that are worth taking
into account, such as:
- Consistent error types for internal functions
- Improvements in the type system and error handling
- Tighter type checks for bitwise / arithmetic operators
- Validation of the abstract trait method
- Correct signatures of magic methods
- Reclassified Engine Warnings
- Opaque objects instead of resources for Curl, Gd, Sockets, OpenSSL, XMLWriter and XML
I encourage you to review the release notes for PHP 8 on the official PHP site if you want to know in-depth about these new resources.
Conclusion
What do you think of these innovations? The truth is
that they seem very interesting and important to me for the future of
PHP. Also, I have the feeling that that feeling - forgive the redundancy -
of writing a lot of code for simple functionality tends to disappear. What
do you think? I hope you understand better about these concepts 8 what is new PHP 8 features, what is new in PHP 8 all you need to know about PHP 8, PHP 8 release date, What changed in PHP 8? attribute review.
However, if you are thinking of using these new resources in
your current project, remember that we are talking about a new major version, and
you would have to change your code first and adapt it to be able to work in PHP
8. Symfony and Drupal are already working on it, and you? Comment
below!






















No comments
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.